Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease is an extremely rare disease that causes dementia and it is estimated that worldwide only one person in every million will contract this disease every year. Diagnosis can be very difficult.
 Fragility of a Dementia Patient
Fragility of a Dementia PatientWhat causes Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease remains unknown and consequently until this is known there can be no known cure. What is known though is that like other dementia causing agents a protein is involved. In this case that protein is called Prion, which is why these variations of CJD are called Prion Diseases.
There can be a very sudden onset of symptoms associated with this neurodegenerative disease and a person can decline rapidly. In the worst cases a person may die in less than a year, although some dementia patients with CJD endure the symptoms for a longer period of time.
Symptoms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
The rapid onset of the symptoms of dementia is an indicator of possible diagnosis of Creutzfeld-Jakob Disease, although it can on a superficial diagnosis be misattributed to being caused by Alzheimer's disease or Huntington's Disease.
Symptoms include impaired memory, thinking, hallucinations, psychosis, heightened anxiety, and slurred speech, depression and a sudden personality change. The physical symptoms of dementia in CJD are involuntary muscle jerks (myoclonus), impaired vision often leading to blindness and eventual loss of all movement. The CJD dementia patient may lose all agency and fall into a coma.
As with most dementia types, death occurs as a consequence of infection, such as pneumonia. An inert bed-ridden dementia patient in coma is prone to Coronary Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD).
Types of CJD
There are a number of types of CJD and these are:
- Sporadic CJD
- Hereditary CJD
- Acquired CJD
- Variants of CJD
Sporadic CJD
Sporadic CJD is the most common form of this dementia causing disease with about 85% of sufferers. It can be regarded as an Early Onset Dementia because it strikes in people as young as forty years of age and its progress is rapid.
Although uncertainty remains around the genesis of all CJDs researchers do not believe that Sporadic CJD has a genetic or infectious cause. It's cause is unknown.
Hereditary CJD
Hereditary CJD, as its name suggests, is caused by a genetic mutation or disorder that is passed down in families. In seeking to identifying diagnose this extremely rare dementia it is important that clinicians investigate the family history of the person presenting with symptoms of dementia.
Acquired CJD
This form of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease is not thought to be transmissible as an infection between humans. However, research identifies it as being contracted as a consequence of contact in medical situations with infected brain or nerve tissue. The virus resists inactivation by boiling water, ultra violet radiation or alcohol. Heat is successful in rendering the virus inactive (121C and 20psi for one hour) Reference link .
This is also called iatrogenic (literal translation: genesis from a doctor).
Variant CJD or New-Variant CJD
This is thought to be caused by eating contaminated meat from cattle infected with what is occasionally still called Mad Cow Disease, correctly known as Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy or BSE.
This seems to affect juveniles rather than older people and the first signs of dementia caused by this variant is psychiatric. New Variant CJD has a longer period duration of progression to death than other versions of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease.
Curiously, variation of this disease was also thought to be transmitted in tribes of Papua New Guinea by cannibalism. It was a disease called kuru that infected women and children more than men.
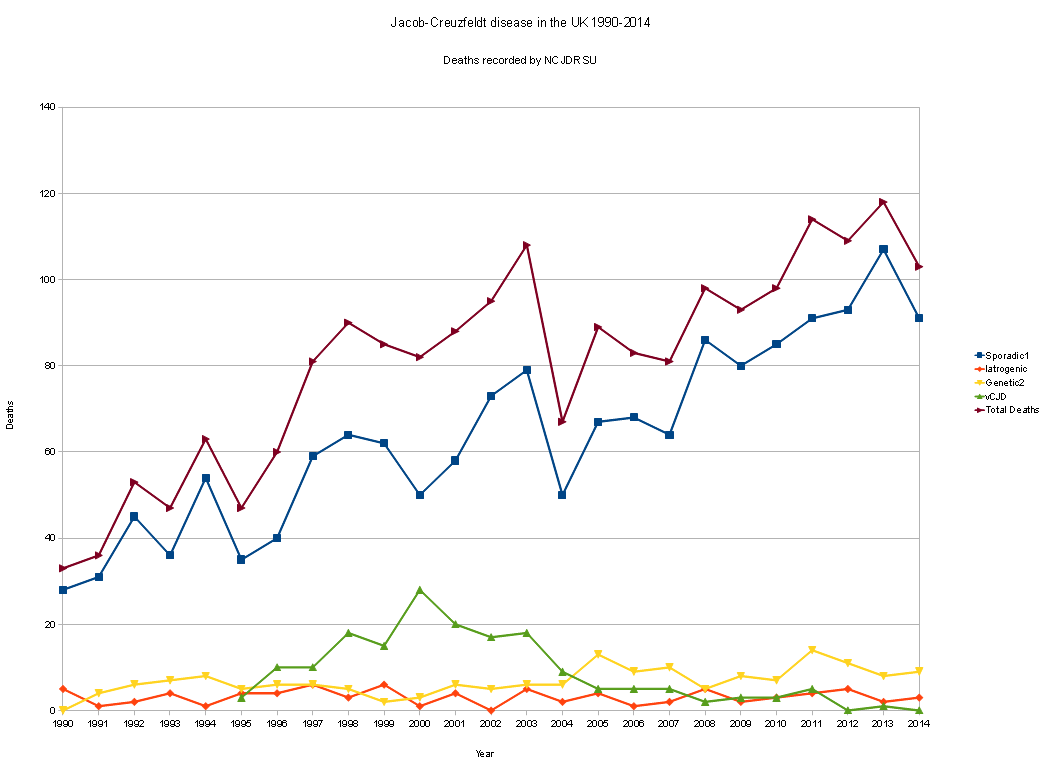 Graph of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Related Deaths
Graph of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Related DeathsCauses of CJD
Unlike many types of dementia - other than the possibility of picking up an infection in specific work related activities - causality for the more prevalent form of the family of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is not known.
Prion is similar to other proteins that inhabit the human body in that they are important to normal functioning; however, in many types of dementia something happens to these proteins that cause them to clump together. This is similar to Tau in Alzheimer's Disease and alpha synuclein in the creation of Lewy bodies in Dementia with Lewy Bodies.
The CJD prion folds in such a manner that they become oddly shaped and insoluble and gather into toxic protein clumps called amyloids, which overwhelm brain tissue by exponential growth and kill off that brain tissue. This destruction of brain tissue and its function is common to all dementias.Exactly what it is that triggers these prions to change is not known. Some suspect a genetic trigger or a virus.
Researchers have long suspected that CJD is caused by a slow virus because of the nature of the disease. CJD is called a TSE Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy because it is one of a group of diseases that can pass from animal to human. Although tests are being developed none have received official ratification yet.
Treatment of CJD
There is no cure for Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, nor for any of its variants. The disease will progress at its invariably rapid pace compared to other dementias and all treatment is specific to the symptoms as they are presented.
Do you have anything you wish to share?
Please feel free to write to me
Return to Dementia Devotion DEMENTIA TYPES Page
Go to HOME PAGE
This website was built with SBI

Recent Articles
-
Dementia Diary. We Must Break Her. It's my name she calls constantly
Dementia Diary. We’ve Got To Break Her.We had all agreed that we had to accept and commit ourselves to the hope that the dementia carers would become her family -
Dementia Diary Page 3. Love, Trauma and Laughter all within minutes
A Dementia Diary. The days that passed were full of Love, Laughter, Kindness and Exquisite Pain. Be ready to weep, laugh and, as usual, hate bastard rabbits. -
Dementia Devotion - Beautiful Karen Carpenter just ran out of time
Dementia Devotion - I keep thinking about beautiful Karen Carpenter who was so caught up in other people's demands that she ran out of time to save herself. -
Betty suffered dementia the last few years and was a very nice lady
Dementia Diary Day 31 Red Squirrels, Rabbits (again) & Suicide Salad - The first news I heard this evening from the Head Nurse, was that Betty had just died -
dementia diary day 30. Has The Mafia Assassin Revealed Her Identity?
Has The Dementia Care Home Assassin Revealed Her Identity? Her right eye was swollen, almost closed and the bruising ran from darkest blue, purple to black -
Dementia Diary Day 20 - Purpose, Futility & Bastard Rabbits!
Dementia Diary Day 20 - Purpose, Futility & the Bastard Rabbits! Eating My Garden







